runtime: WinHttpException on WebRequest
The following snippet of code call a web service using a certificate from the user store. I got a generic security exception
System.Net.Http.WinHttpException (0x80072F8F): A security error occurred
with NativeErrorCode 12175. The same snippet works against .NET Framework 4.6.1.
Any guidance on troubleshooting this issue?
using (var store = new X509Store(StoreName.My, StoreLocation.CurrentUser))
{
store.Open(OpenFlags.ReadOnly);
var cert = store.Certificates.Find(X509FindType.FindBySerialNumber, "serial_number", false);
HttpWebRequest request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create("https://url");
request.ClientCertificates.Add(cert[0]);
request.Method = "GET";
request.ServerCertificateValidationCallback = delegate
{
// I know this is unsafe
return true;
};
HttpWebResponse response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
var encoding = Encoding.UTF8;
using (var reader = new StreamReader(response.GetResponseStream(), encoding))
{
string responseText = reader.ReadToEnd();
}
}
[EDIT] C# syntax highlighting by @karelz
About this issue
- Original URL
- State: closed
- Created 6 years ago
- Comments: 16 (8 by maintainers)
Actually I’m still waiting for the new certificate from the other party. I will reopen the issue if needed. Thanks for your support.
That is by-design behavior of .NET Core. And latest versions of .NET Framework behave the same.
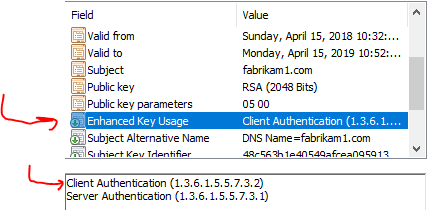
If there is an EKU (Enhanced Key Usage) X509v3 extension on the certificate, then it must have the ClientAuthenticationOid present. If there is no EKU extension at all, then it means the cert is valid for all EKU purposes.
So, the fix here is to make sure to either not include an EKU at all (not recommended) or make sure that ClientAuthenticationOid is present on the EKU extension.
Example: